
As we commented, Athena is great for relatively simple ad hoc queries in S3 data lakes even when data is large, but there are situations (complex queries, heavy usage of reporting tools, concurrency) in which it is important to consider alternative approaches, such as data warehousing technologies. In our second article, we introduced Athena and its serverless querying capabilities. The rest of tables are left unpartitioned. Partitioned Parquets: 32.5 GB – the largest tables, which are partitioned, are lineitem with 21.5GB and orders with 5GB, with one partition per day each partition has one file and there around 2,000 partitions per table.Parquets without partitions: 31.5 GB – the largest tables are lineitem with 21GB and orders with 4.5GB, also split into 80 files.Raw (CSV): 100 GB – the largest tables are lineitem with 76GB and orders with 16GB, split into 80 files.In that example, we used a dataset from the popular TPC-H benchmark, and generated three versions of the TPC-H dataset:
Distribution key redshift how to#
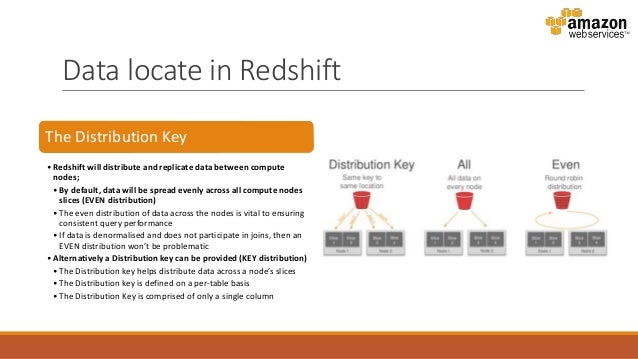
We also introduced the concept of the data lakehouse, as well as giving an example of how to convert raw data (most data landing in data lakes is in a raw format such as CSV) into partitioned Parquet files with Athena and Glue in AWS. In the first article of the series, we discussed how to optimise data lakes by using proper file formats ( Apache Parquet) and other optimisation mechanisms (partitioning). The schema, that contains the table, has to be in the search path.This is the third article in the ‘Data Lake Querying in AWS’ blog series, in which we introduce different technologies to query data lakes in AWS, i.e. SORTKEY and DISTKEY created for a table in Redshift can be checked with a query like this (to be executed directly on Redshift). ALL distribution can improve execution time when used with certain dimension tables where KEY distribution is not appropriate, but performance improvements must be weighed against maintenance costs. This distribution style ensures that all the rows required for any join are available on every node, but it multiplies storage requirements and increases the load and maintenance times for the table. If you specify DISTSTYLE KEY, you must name a DISTKEY column.ĪLL: A copy of the entire table is distributed to every node. When data is collocated, the optimizer can perform joins more efficiently. When you set the joining columns of joining tables as distribution keys, the joining rows from both tables are collocated on the compute nodes. KEY: The data is distributed by the values in the DISTKEY column. Row IDs are used to determine the distribution, and roughly the same number of rows are distributed to each node. It is not possible to specify more than one DISTKEY for each recommended optimization.ĮVEN: The data in the table is spread evenly across the nodes in a cluster in a round-robin distribution. Dist KeysĭISTKEYs are not automatically recommended by the system and they need to be manually created by the user. The system will create then a SORTKEY with one column or with multiple columns if the highest freq index is SINGLE or MULTIPLE, respectively.Ĭolumns that are normally recommended for index creation are used to define dist and sort keys. Since it is possible to specify only one SORTKEY(with one or more columns) at the table level, we decided to create a SORTKEY corresponding to the recommended index (with kind SINGLE or MULTIPLE) with the highest frequency. SORTKEYs are created analyzing the currently recommended indexes collected for each optimization.Īccording to the documentation, SORTKEYs can be specified both at column and table levels. It is possible to specify only one SORTKEY column (at column level) or multiple columns if defined at the table level. With respect to indexes, distkeys and sortkeys must be defined when the table is created.

Redshift does not support indexes but supports distribution and sort keys that can be used to improve the performance of queries. BucketPrefix translator property is available since 2.1.7ĬreateBucket translator property is available since 2.1.15


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
